Negative Retained Earnings: Definition, Impacts, and Effects

Instead, they reallocate a portion of the RE to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts. This allocation does not impact the overall size of the company’s balance sheet, but what does negative retained earnings mean it does decrease the value of stocks per share. Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account. These reduce the size of a company’s balance sheet and asset value as the company no longer owns part of its liquid assets.
- Retained earnings represent the portion of the cumulative profit of a company that the business can keep or save for later use.
- That net income lets the company distribute money to shareholders or use it to invest in its own growth.
- Generally speaking, a company with a negative retained earnings balance would signal weakness because it indicates that the company has experienced losses in one or more previous years.
- This scenario may signal financial risk or insolvency to creditors and investors.
- At first glance, it might seem like investors would frown upon retained earnings because it means a company isn’t paying out its profits in the form of dividends.
- The account normally has a credit balance, which is caused by the cumulative generation of profits over time.
The retained earnings formula is:
If a company’s retained earnings are less than zero, it is referred to as an accumulated deficit. This may be the Interior Design Bookkeeping case if the company has sustained long-term losses or if its dividends exceed its profits. Profits give a lot of room to the business owner(s) or the company management to use the surplus money earned.
Are retained earnings equity?

Your investment decisions should normal balance be justified by the valuations of the companies in which you invest. If the stock appears overvalued and there is a high degree of uncertainty about its business prospects, it may be a highly risky investment. For example, the toy manufacturing company may have spent $3 million to produce those toys, but that’s not reflected in its revenue. Dividends can only be paid out of retained profits (i.e. profits left in the business after corporation tax has been paid).
Net Fixed Assets and Their Impact on Financial Analysis

The RE balance may not always be a positive number, as it may reflect that the current period’s net loss is greater than that of the RE beginning balance. Alternatively, a large distribution of dividends that exceed the retained earnings balance can cause it to go negative. It can reinvest this money into the business for expansion, operating expenses, research and development, acquisitions, launching new products, and more. The specific use of retained earnings depends on the company’s financial goals. Ultimately, the company’s management and board of directors decides how to use retained earnings. When a company generates net income, it is typically recorded as a credit to the retained earnings account, increasing the balance.
These include revenues, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and depreciation. As a result, additional paid-in capital is the amount of equity available to fund growth. And since expansion typically leads to higher profits and higher net income in the long-term, additional paid-in capital can have a positive impact on retained earnings, albeit an indirect impact. To improve negative retained earnings, a company may need to focus on increasing revenue, reducing expenses, and improving its overall financial management. This could involve implementing cost-cutting measures, finding new sources of income, or restructuring the business to be more efficient.
Negative retained earnings often arise from a company’s prolonged inability to generate a profit, which can be due to a variety of operational or external factors. For example, a business may experience a downturn in sales due to increased competition, leading to reduced revenue and, consequently, losses. Alternatively, operational inefficiencies, such as high production costs or wasteful spending, can erode profits over time, pushing retained earnings below zero.
- However, it’s essential to understand that these earnings may not necessarily reflect the company’s available cash.
- A company that is consistently able to maintain profitable operations will generally see its figure grow over the years.
- To simplify your retained earnings calculation, opt for user-friendly accounting software with comprehensive reporting capabilities.
- A cash dividend results in a cash outflow and reduces the company’s liquid assets, while stock dividend distributions transfer retained earnings to common stock.
- Further, figuring your retained earnings helps your company work out cash projections and draw up a budget for the year ahead, which will also be necessary to shareholders.
It’s important to note that retained earnings are cumulative, meaning the ending retained earnings balance for one accounting period becomes the beginning retained earnings balance for the next period. This approach allows organizations to effectively lower costs and identify areas where expenditures can be trimmed without sacrificing quality or productivity. By optimizing cost structures and streamlining operations, companies can create a leaner and more efficient business model. This not only impacts the immediate bottom line but also sets the foundation for sustained profitability and growth. By proactively managing resources and expenses, businesses can navigate economic uncertainties and market fluctuations with greater resilience. One of the key strategies to improve negative retained earnings is by increasing profits through revenue growth and effective expense management.
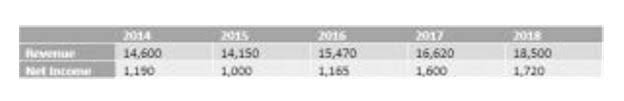
What is a Retained Earnings Deficit?
Net profit refers to the total revenue generated by a company minus all expenses, taxes, and other costs incurred during a given accounting period. Revenue, net profit, and retained earnings are terms frequently used on a company’s balance sheet, but it’s important to understand their differences. Company B faced negative retained earnings following a series of failed investments and economic downturns, necessitating a reevaluation of its financial position and strategic direction. To increase profitability, companies should focus on maximizing revenue through product diversification, expanding market reach, and implementing cost-saving measures. Optimizing capital allocation involves evaluating investment opportunities, reducing debt levels, and efficiently managing working capital.


